How It Works
The algorithm takes an input file and converts it into a compressed binary file.
It is a greedy algorithm that tries to map more frequent characters with a smaller number of bits and less frequent characters with a larger number of bits.
Below is a mapping we would want to achieve:
| Char | Code | Freq | Total Bits |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 110 | 10 | 30 |
| E | 10 | 15 | 30 |
| I | 00 | 12 | 24 |
| S | 11111 | 3 | 15 |
| T | 1110 | 4 | 16 |
| P | 01 | 13 | 26 |
| \n | 11110 | 1 | 5 |
To do this we want the encoding scheme to be a min heap (binary tree where parent node value is always greater than child node value).
Each node represents a frequency.
Every time we traverse left in the tree, we append a 0 bit, everytime we traverse right, we append a 1 bit

First create a table mapping characters to its frequency
| Char | Freq |
|---|---|
| A | 10 |
| E | 15 |
| I | 12 |
| S | 3 |
| T | 4 |
| P | 13 |
| \n | 1 |
Then take the two lowest frequencies and make them the children of a parent node whose value is the sum of its children.
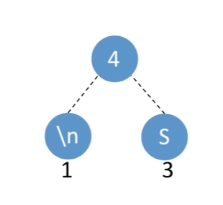
Continuing…
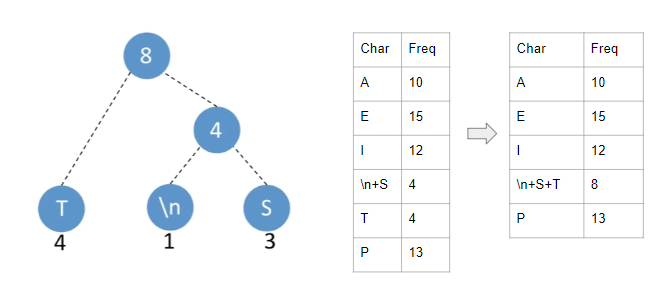
Until one entry left
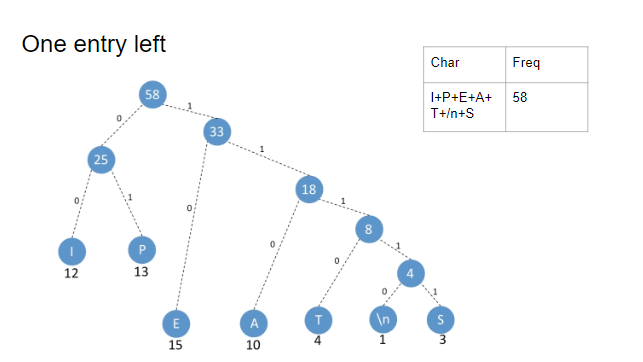
Traverse the tree and get the codes then encode the text
Text:
ASSSAAAAEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEIIIIIIIIIIIIAAAAATTTTPPPPPPPPPPPPP\n
Bits:
11011111111111111111011011011010101010101010101010101010101000000000000000000000000011011011011011011101110111011100101010101010101010101010111110
Result
- original bit length
- 464 (58 * 8)
- encoded bit length
- 146